6 Strong Solutions to Monitor No Sound HDMI Problems
Having no sound from your monitor when connected via HDMI can be frustrating. Fortunately, there are several troubleshooting…
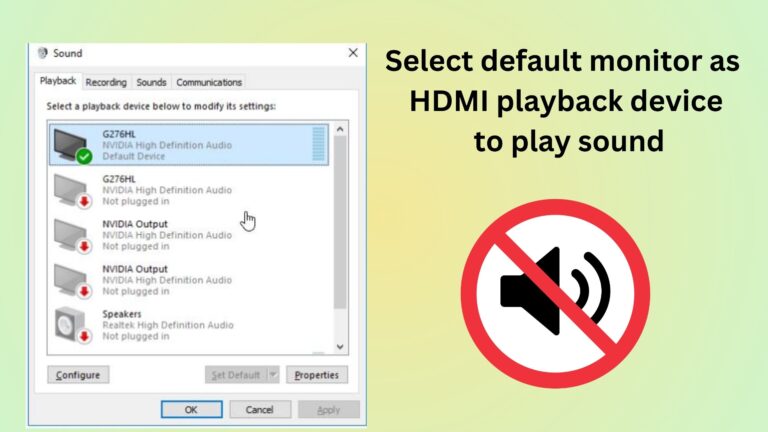
Having no sound from your monitor when connected via HDMI can be frustrating. Fortunately, there are several troubleshooting…
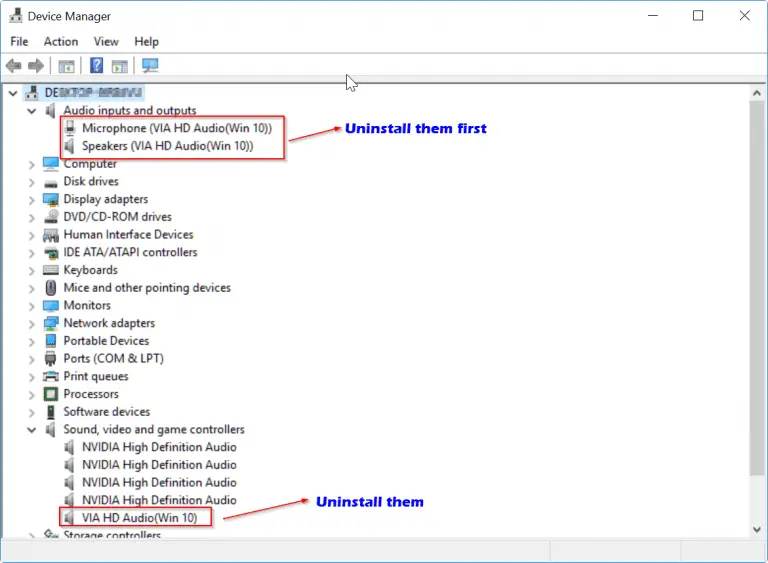
HDMI Audio drivers for Windows 10 are not easy to find automatically. Sound issues on HD connection or…
The first thing to check when your windows 11 bluetooth is not working is whether it’s turned on….
The best privacy settings for Facebook send the right signals to your friends. You can reduce notifications, annoying…
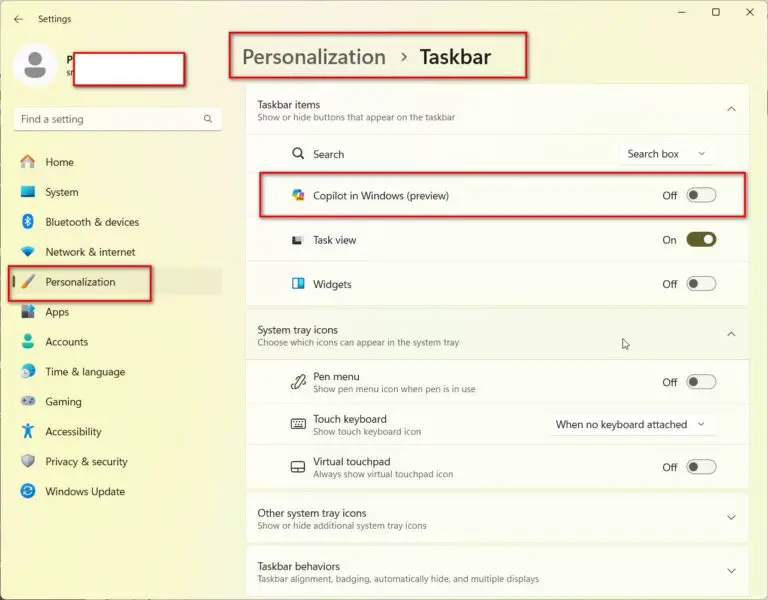
AI-powered virtual assistant introduced by Microsoft as part of the new operating system. Sometimes it can be annoying….
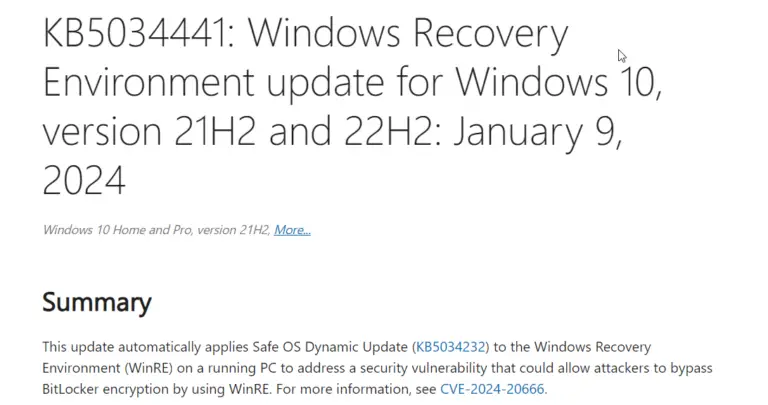
The error code 0x80070643 is a common issue encountered by Windows 10 users when attempting to install updates…
In the realm of digital workspaces, a dual monitor setup under Windows 10 can dramatically improve your productivity….

In today’s fast-paced, multitasking world, having a dual monitor setup can significantly boost your productivity and efficiency. Windows…
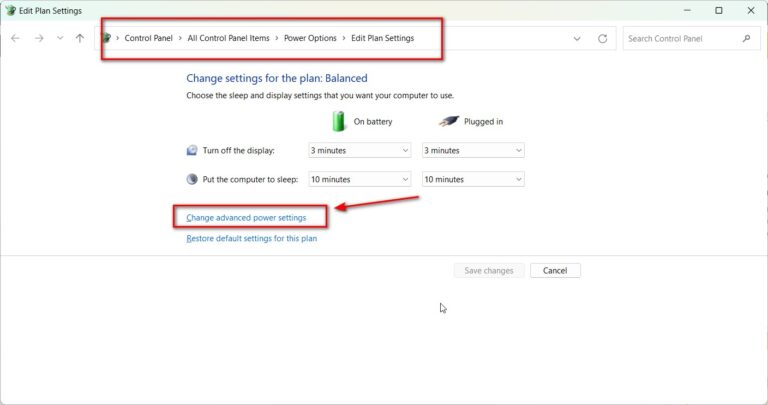
The Power Options menu in Windows 11 allows you to manage power plans and set basic options like…
Windows 11 introduced a new Power Mode feature that allows you to choose between best battery life, best…