Video output settings play a crucial role in determining the quality and performance of videos, whether you are watching on a TV, gaming console, or computer.
These settings control key parameters such as resolution, frame rate, bitrate, and video codecs, ensuring that the video signal is transmitted effectively and with optimal quality.
Understanding how to configure video output settings is not just about getting the right picture quality. It’s also about ensuring that your device and the hardware you’re using are aligned for the best possible performance.
For example, a high-quality video signal may be wasted if the device isn’t capable of handling it or if the settings aren’t correctly matched to the display.
In this guide, we’ll explore how these settings work, why they matter, and how you can adjust them to get the best experience across different devices, whether it’s a TV, gaming console, laptop, or PC.
We’ll also highlight some of the most common video output hardware and provide you with tips to fine-tune these settings based on your specific use case, such as gaming, watching high-definition movies, or video editing.
Key Areas We’ll Explore:
- Resolution: Understanding the number of pixels displayed on your screen and how it affects clarity and detail.
- Frame Rate: The number of frames per second that a video displays, which influences motion smoothness and visual fidelity.
- Bitrate: The amount of data transmitted per second of video, directly affecting both quality and bandwidth requirements.
- Video Codecs: The technology behind compressing and decompressing video files, determining the video format for playback.
Each of these parameters works in conjunction to create a seamless video output experience. Misadjustments can result in visual artifacts, buffering, and suboptimal performance.
With proper settings, you can enhance video quality, minimize lag, and ensure a more enjoyable viewing or gaming experience.
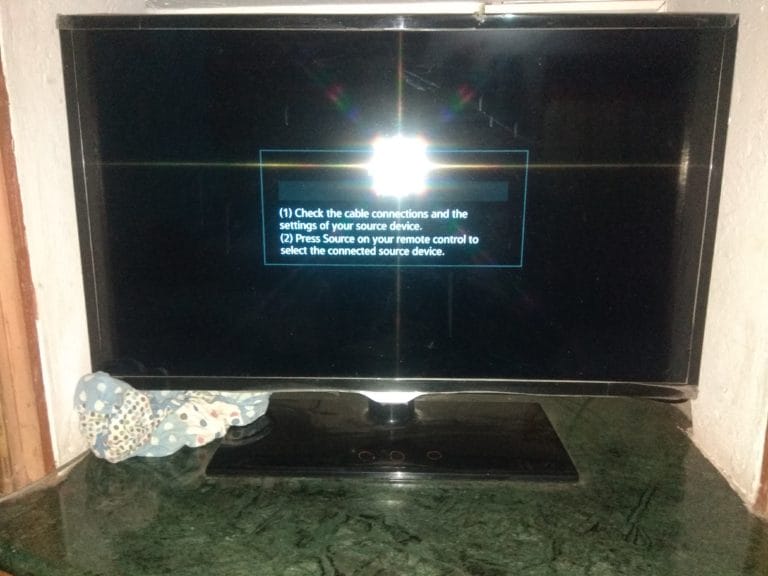
Video Output Settings on a TV
When it comes to TV viewing, video output settings are essential for enhancing the picture quality, ensuring that the video plays correctly according to your TV’s capabilities. Several factors contribute to the overall video performance, including resolution, input connector type, and supported video modes.
Resolution
The resolution refers to the number of pixels that make up the video frame. Higher resolution results in a sharper image, but it requires more processing power and bandwidth. For instance, 4K resolution provides significantly more detail compared to Full HD (1080p), but streaming services or TV hardware must support the higher resolution to achieve the desired quality.
- 4K (Ultra HD): 3840 x 2160 pixels
- Full HD (1080p): 1920 x 1080 pixels
- HD (720p): 1280 x 720 pixels
If you have a 4K-capable TV but are only watching content in 1080p, the TV will upscale the resolution to fit its display, but the picture quality will not match native 4K content. Adjusting resolution settings allows you to get the most out of your TV and ensures the best picture possible for your video source.
Input Connector
Different devices use various cables to connect to the TV. These cables transfer the video signal from the source to the display. Common input connectors include:
- HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface): The most common and versatile input for modern TVs and gaming consoles. It supports high-definition video and audio.
- VGA (Video Graphics Array): An older connection typically used in legacy computers and some projectors.
- DisplayPort: Often used for computers and high-end gaming setups.
The choice of input connector affects the video signal quality. For example, HDMI supports both video and audio over a single cable, making it the preferred choice for most modern setups.
Supported Video Modes
Your TV may support various video modes, such as 720p, 1080p, or 4K, depending on the model. You need to ensure that the output settings on your device match the capabilities of your TV for the best viewing experience. Many modern TVs support HD, 4K, and even HDR (High Dynamic Range) modes, allowing for superior color depth and contrast.
Video Output Settings on a Gaming Console
Gaming consoles are another device where video output settings are paramount. These settings determine the quality of the video signal sent from the console to your TV, ensuring smooth gameplay and optimal visual quality. Adjusting settings such as frame rate and resolution can drastically impact your gaming experience.
Video Output Settings
Gaming consoles like PlayStation, Xbox, and Nintendo Switch offer configurable video output settings. These settings help you match the console’s output with your TV’s capabilities. Here are some key settings:
- Resolution: Ensure the console is set to output at the resolution supported by your TV (e.g., 4K or 1080p).
- HDR: High Dynamic Range offers better contrast and color accuracy. Ensure HDR is enabled on both your console and TV for a stunning visual experience.
- Frame Rate: Most consoles allow you to choose between different frame rates, such as 30Hz, 60Hz, or higher. For a smoother gaming experience, higher frame rates (e.g., 60Hz or 120Hz) are preferable.
Supported Video Modes
Just as with TVs, gaming consoles support various video modes. For instance, the Xbox Series X and PlayStation 5 support 4K resolution at 120Hz, which requires an HDMI 2.1 cable to fully utilize. It’s essential to check the supported video modes and match the console’s output to your TV’s capabilities.
Technical Video Output Parameters
There are various technical settings that affect video output quality and performance. Adjusting these parameters can optimize video playback for both streaming and gaming.
Output Video Bitrate
Video bitrate refers to the amount of data processed per second of video playback. A higher bitrate results in better video quality but requires more bandwidth. It’s especially crucial when streaming high-definition content or gaming online. If your connection speed is limited, you may need to lower the bitrate to prevent buffering.
GOP Size
GOP (Group of Pictures) is a term used in video compression. The GOP size determines the frequency of keyframes in the video stream. A shorter GOP size can improve video quality, especially during fast-moving scenes, but it may increase file size. A longer GOP size is used to reduce file size without a noticeable impact on quality.
Force Key Frames
In video encoding, keyframes serve as reference points for subsequent frames. Forcing keyframes ensures that the video quality is maintained even if there’s significant movement in the video. For live streaming or fast-moving content, forcing keyframes can help reduce visual artifacts.
Frame Width & Frame Height
These settings control the dimensions of the video frame. Adjusting frame width and frame height impacts the overall video quality and aspect ratio. For example, you may want to adjust the frame width to match the native resolution of your TV (e.g., 1920 for Full HD or 3840 for 4K).
Slices
Slices are segments of video frames that can be independently decoded. In encoding, slices can help distribute processing power across multiple cores, improving performance and reducing latency during video playback. This setting is especially important for streaming videos or encoding large files.
Cores
The number of cores used for encoding video affects processing speed and efficiency. More cores typically lead to faster encoding times and better video output quality, especially when handling high-definition video or complex video streams.
Preset
A preset determines the encoding speed and quality balance. Faster presets prioritize encoding speed, while slower presets provide higher video quality at the expense of processing time. The choice of preset depends on your hardware capabilities and the level of quality required.
Tune
The tune setting allows you to optimize video encoding for specific types of content. For example, you can set it to “film” for movies or “animation” for animated content, allowing for better color accuracy and reduced artifacting.
CRF (Constant Rate Factor)
The CRF setting controls the balance between video quality and file size. A lower CRF value results in higher quality, while a higher CRF value compresses the video more, reducing quality. For streaming or archiving, a CRF value between 18-28 is typically recommended.
Pixel Format
The pixel format defines how color information is stored for each pixel. Common formats include YUV420 and RGB. The choice of pixel format affects both video quality and compatibility with different devices.
Frame Rate & Output FPS
Frame rate plays a vital role in the smoothness of the video. For general viewing, 30 fps is often sufficient, but for gaming or action scenes, a higher frame rate like 60 fps or 120 fps may be necessary for a more fluid and realistic experience.
TV Output Settings
For optimal performance, you must configure the correct settings for TV output.
Set the Television Aspect Ratio and Signal Format
When connecting a device to a TV, you must adjust the aspect ratio and signal format for compatibility.
- Aspect Ratio: Most modern TVs use a 16:9 aspect ratio, but some older TVs may use 4:3. Adjust this setting accordingly in the TV’s menu.
- Signal Format: Depending on your location, you may need to set the signal format to either NTSC or PAL, which are two video encoding standards used in different regions.
To adjust these settings on your TV:
- From the HOME menu, go to Settings.
- Select Video Settings.
- Adjust TV output size (16:9 or 4:3).
- Choose the appropriate signal format (NTSC or PAL).
Internet Connection and Recommended Encoding Settings
If you’re streaming content or video chatting, it’s crucial to ensure your internet connection and encoding settings are optimized for video output.
Recommended Encoding Settings
Choosing the right encoding settings ensures smooth playback, reduces lag, and prevents buffering during streaming.
- Video Resolution: Always select the highest resolution supported by your internet speed and device capabilities.
- Video Bitrate: Choose a bitrate that balances quality with bandwidth availability. For 4K streaming, a bitrate of 15-25 Mbps is recommended.
- Audio Bitrate and Sample Rate: Higher audio bitrates result in better sound quality. A 128kbps audio bitrate is typically sufficient for general purposes, but 256kbps or higher is ideal for high-quality streaming.
Frame Rate and Video Codec
The frame rate should be set to 30 fps for general content and 60 fps for high-motion or gaming content. The most commonly used video codec is H.264, which provides excellent compression without sacrificing quality.
Keyframe Interval and Audio Codec
A keyframe interval of 2-4 seconds is recommended for most video streaming platforms. For audio codec, AAC is widely used, offering a good balance between file size and sound quality.
Streaming Protocols
Various streaming protocols, such as RTMP, HLS, and MP4, are used for live video transmission. Each has its advantages depending on the type of content being streamed and the network setup.
Conclusion
Video output settings are integral to ensuring optimal performance whether you’re watching TV, gaming, or streaming content. By adjusting resolution, frame rate, bitrate, and other key settings, you can significantly enhance your viewing or gaming experience. Understanding and configuring the right video output settings can help you get the most out of your hardware and provide superior video quality across devices. Always ensure your settings match your device’s capabilities for the best possible video output.